Ever wondered how a seemingly small component can dictate the performance and efficiency of complex industrial processes? Vacuum solenoid valves are precisely that unsung heroes working tirelessly behind the scenes. These valves are the silent architects of controlled environments, ensuring the smooth operation of countless systems.
In an era defined by technological advancement, understanding these often-overlooked devices is critical. Vacuum solenoid valves are not mere components; they are the gatekeepers of precision, automation, and safety across a multitude of sectors. From the bustling automotive industry to the intricate world of manufacturing, these valves are indispensable, orchestrating the precise movements of fluids and gases under vacuum conditions. This guide delves deep into the world of vacuum solenoid valves, unveiling their inner workings, diverse applications, and the reasons they have become a cornerstone of modern engineering.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Functionality | Precisely controls the flow of fluids or gases by creating or releasing a vacuum within a system. This control is essential for many industrial processes that require specific vacuum levels. |
| Key Industries | Automotive, Manufacturing, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), Medical Equipment, and various laboratory and research settings. |
| Operational Principle | Operates using an electromagnetic force. When energized, the solenoid coil generates a magnetic field that moves a plunger, which in turn opens or closes the valve. |
| Types of Valves | Direct Acting, Pilot Operated, Two-Way, and Three-Way valves. Each type is designed for specific pressure and application requirements. |
| Material Considerations | Materials must be compatible with the fluids or gases handled. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and various plastics. Material selection impacts valve lifespan and performance. |
| Common Issues | Leaking, sticking plungers, and electrical failures are the most commonly reported issues. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Regular inspection of seals and gaskets, cleaning the valve, and checking electrical connections are vital. Preventive maintenance can significantly extend valve life. |
| Future Trends | Expect to see enhanced automation, improved materials, and increased energy efficiency. Innovations in valve design will continue to drive advancements. |
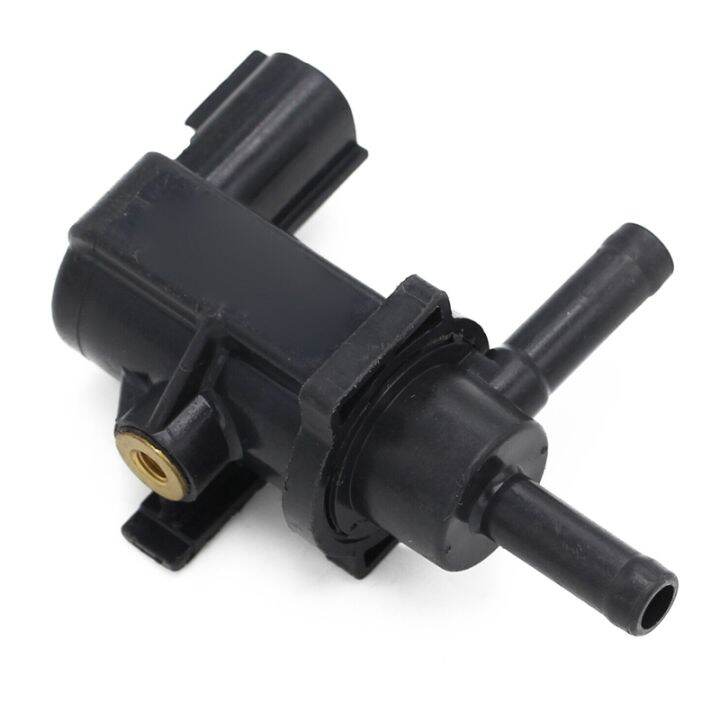
A vacuum solenoid valve, at its core, is an electromechanical marvel designed to regulate the flow of fluids or gases by meticulously managing vacuum levels. Imagine a tiny gatekeeper, opening and closing with precision to maintain the delicate balance within a system. This valve is far more than just a component; it is an essential element in industrial applications where precision and control are paramount.
- Speedex Tracking Your Ultimate Guide For Realtime Parcel Monitoring
- Shadow Milk Cookie Plush The Ultimate Guide For Fans Collectors
These valves are not created equal, each engineered for specific operational demands. They are engineered to thrive in low-pressure environments and high-vacuum applications, operating efficiently within these conditions. This specialization has made vacuum solenoid valves indispensable across a variety of sectors including automotive, manufacturing, and HVAC.
Their importance stems from their vital role in maintaining system integrity and performance. Precise control over vacuum levels ensures processes operate seamlessly and efficiently. Furthermore, these valves contribute to energy conservation and enhanced safety in a diverse range of applications.
The fundamental functionality of a vacuum solenoid valve is centered around the control of fluid or gas flow, achieved through either the creation or the release of a vacuum. In simpler terms, it's a system of on/off control, allowing fluids and gases to enter or exit the system based on the specific requirements. This ability to provide precise control over vacuum levels is critical for the optimized performance of systems that heavily rely on vacuum technology.
- Tiktok Archive How To Manage Optimize Your Content
- Dti Jewelry Overload Your Ultimate Guide To Smart Buys
The operation of a vacuum solenoid valve depends on electromagnetic force. An electrical current energizes the solenoid coil, generating a magnetic field. This field then activates the plunger, causing it to move and either open or close the valve. This precise movement is the key to controlling the flow of fluids and gases.
The selection of the right vacuum solenoid valve is application-specific, with different types designed to cater to specific needs. The types of vacuum solenoid valves most commonly found are:
- Direct Acting Valves
- Pilot Operated Valves
- Two-Way Valves
- Three-Way Valves
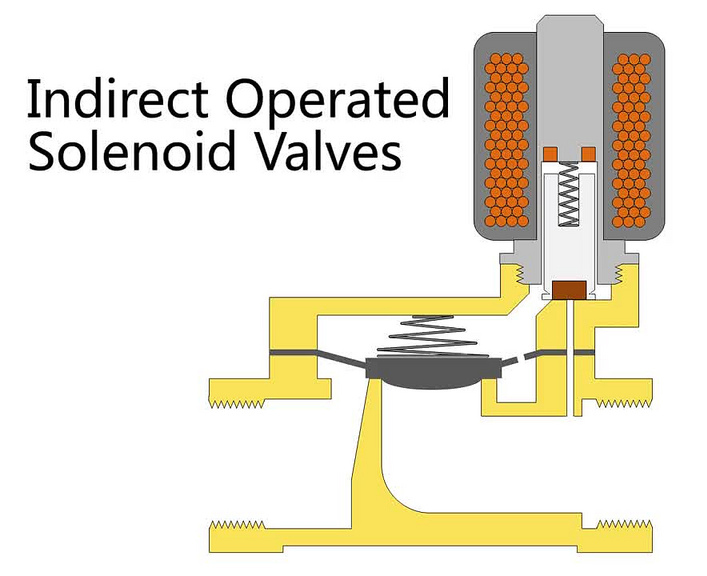
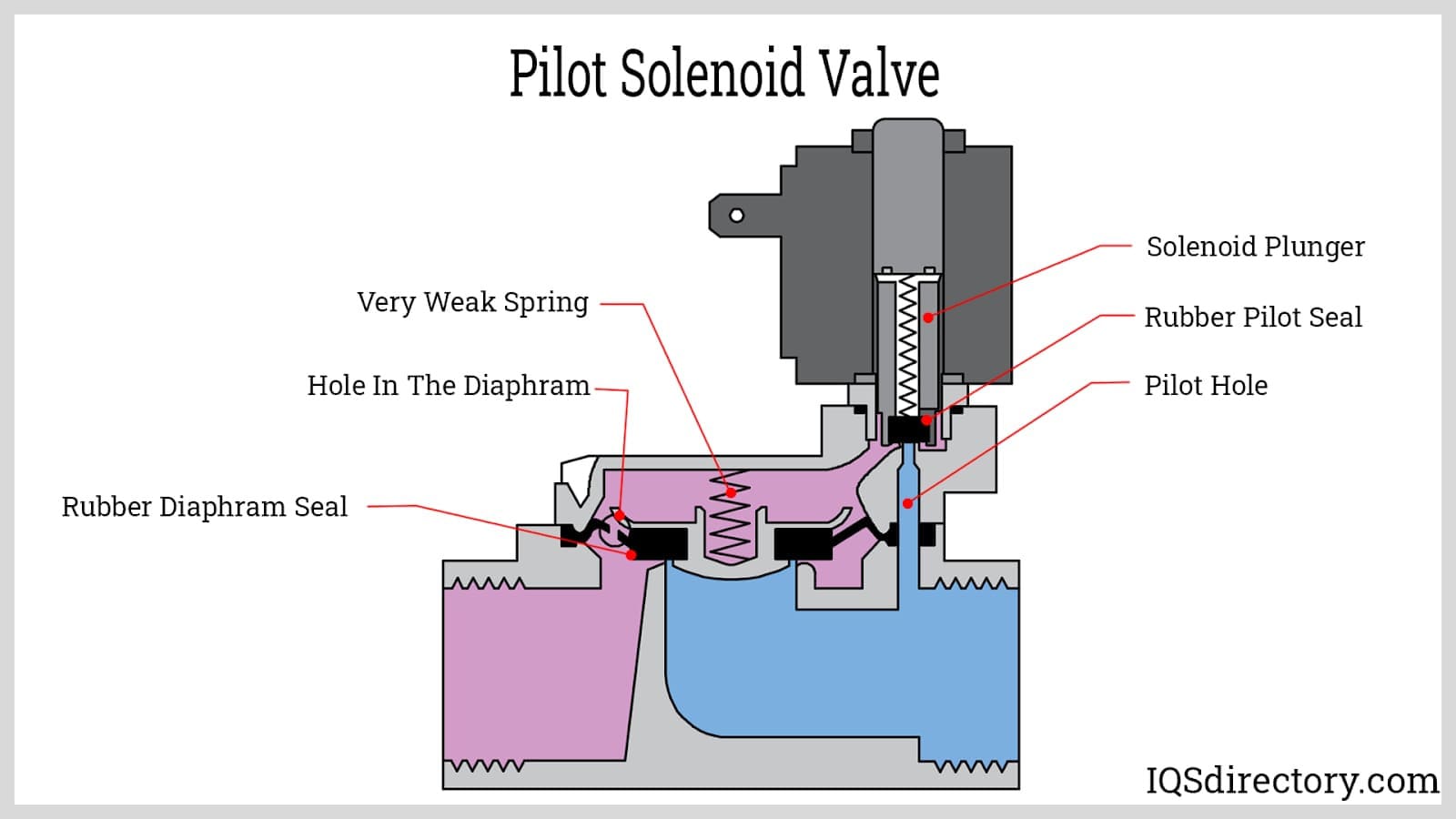
Direct acting valves use the solenoid coil to directly move the plunger. They're ideally suited for low-pressure applications. Pilot operated valves, on the other hand, utilize system pressure to assist the opening and closing process. This makes them a perfect choice for high-pressure environments, where greater force is necessary to maintain functionality.
The operational principle of a vacuum solenoid valve relies on electromagnetic force. When the solenoid coil is energized, it produces a magnetic field, that actuates the plunger. This action precisely controls vacuum levels, critical for safe and efficient system operation. The construction and design of the valve, along with its choice of materials, are crucial for its long-term performance and durability.
Understanding the different components that make up a vacuum solenoid valve is essential in order to select the right valve for your specific application:
- Solenoid Coil
- Plunger
- Valve Body
- Seal
Vacuum solenoid valves find a broad range of applications across industries. Here are a few examples:
- Automotive Systems
- Manufacturing Processes
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
- Medical Equipment
In the automotive industry, these valves are vital in engine management systems. They ensure the optimal control of vacuum levels, thus boosting fuel efficiency. Additionally, they are used in braking systems, increasing safety and overall performance.
The benefits of incorporating vacuum solenoid valves into a system are considerable. Some key advantages include:
- Precise Control Over Vacuum Levels
- High Reliability and Durability
- Energy Efficiency
- Improved Safety and Performance
Vacuum solenoid valves outperform other valve types when it comes to performance and reliability. Their capacity to finely manage vacuum levels is crucial, ensuring peak performance and minimizing operational errors.
Selecting the correct vacuum solenoid valve demands a thorough assessment of key criteria, including:
- Operating Pressure and Temperature
- Material Compatibility
- Electrical Requirements
- Valve Type and Configuration
The materials used to construct your vacuum solenoid valve significantly impact its lifespan and performance. Common materials are:
- Brass
- Stainless Steel
- Plastic
Even the most dependable equipment can experience issues. These issues often manifest in the form of:
- Leaking Valves
- Sticking Plungers
- Electrical Failures
Troubleshooting these issues involves checking the valve's seals and confirming their integrity. Then, inspect the plunger for any signs of wear or damage, and replace it if necessary. Finally, you must verify the electrical connections and replace any defective parts.
To guarantee consistent performance, regular maintenance is necessary. Some of the maintenance tips include:
- Inspecting Seals and Gaskets
- Cleaning the Valve Regularly
- Checking Electrical Connections
A preventive maintenance strategy can help identify potential problems before they escalate. Such a proactive strategy will save you both time and money, and ensure that your systems continue to perform optimally.
The future of vacuum solenoid valve technology will see continued advancement, leading to enhanced efficiency and reliability. Some trends to watch include:
- Improved Materials and Construction
- Enhanced Automation and Connectivity
- Increased Energy Efficiency
Ongoing innovation in valve design ensures vacuum solenoid valves will become more versatile, adaptable, and efficient, meeting the evolving needs of modern systems.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Vacuum | A space devoid of matter, or a space in which the pressure is significantly lower than atmospheric pressure. |
| Solenoid Coil | A coil of wire used to generate a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. This field actuates the valve. |
| Plunger | A movable core within the solenoid coil that opens or closes the valve in response to the magnetic field. |
| Direct Acting Valve | A valve that uses the solenoid coil to directly move the plunger to open or close the valve. |
| Pilot Operated Valve | A valve that uses system pressure to assist in opening and closing the valve, suitable for high-pressure applications. |
| Two-Way Valve | A valve with two ports one for inlet and one for outlet used to control the flow of fluid or gas. |
| Three-Way Valve | A valve with three ports that can direct the flow of fluid or gas between different paths or release it to the atmosphere. |
The continued advancement of vacuum solenoid valve technology is a testament to the demands of precision engineering. These valves are not merely components, they are the silent architects that enable automation, enhance safety, and improve energy efficiency. By providing precise control over vacuum levels, these valves are critical to a wide range of industrial applications. Their role is often understated, but their impact is significant, helping to ensure the smooth and efficient operation of numerous critical systems.
Engineering Toolbox,ScienceDirect,Industrial Vacuum
- Find Somali Restaurants Near You A Flavorful Guide
- Unveiling Samantha The Oracle Llc Your Guide To Spiritual Insights