Is a nagging cough leaving you doubled over in abdominal pain? It's a common ailment, and understanding why is the first step towards finding relief.
Abdominal pain triggered by a cough can be an unsettling experience, often raising concerns about the underlying cause. While it's frequently dismissed as a minor inconvenience, this discomfort can sometimes signal a deeper health issue that warrants attention. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the phenomenon of abdominal pain when coughing, offering insights into its origins, diagnosis, and available treatment options. We'll explore the various factors that contribute to this discomfort, from simple muscle strains to more complex medical conditions, empowering you with the knowledge to effectively address your concerns.
| Name | Abdominal Pain When Coughing |
| Symptoms | Sharp or dull pain in the abdomen, increased pain during or after coughing, bloating or gas, nausea or vomiting, difficulty breathing. |
| Common Causes | Muscle strain, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Hernias |
| Diagnosis Methods | Medical History, Physical Examination, Diagnostic Tests (Ultrasound, CT scan, Endoscopy, Blood tests) |
| Treatment Options | Medications (Anti-inflammatory drugs, Antacids, Pain relievers), Surgical Intervention (for hernias) |
| Self-Care Tips | Rest and Recovery, Gentle Stretching, Dietary Adjustments |
| Prevention | Practice good posture, Stay hydrated, Avoid smoking |
| When to see a doctor | Persistent or worsening pain, Fever or chills, Severe nausea or vomiting, Blood in vomit or stool. |
| Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Relief | Regular Exercise, Stress Management, Healthy Diet |
| Reference | Mayo Clinic |
The human body is a complex network, and understanding the interplay of its systems is key to deciphering the causes of abdominal pain related to coughing. The abdominal region houses crucial organs like the stomach, intestines, liver, and kidneys. When a cough occurs, the diaphragm, a major muscle involved in breathing, contracts forcefully. This action increases the pressure within the abdomen, a phenomenon known as intra-abdominal pressure. This increased pressure can exacerbate existing conditions or, in some instances, lead to new discomfort.
- Taylor Swifts Dance A Deep Dive Into Her Iconic Performances
- Two Strand Twist Dreads A Complete Guide Your Brand
Furthermore, the abdominal muscles, responsible for stabilizing the core during movements including coughing, also play a significant role. Repeated, forceful coughing can strain these muscles, resulting in soreness and pain. The severity of the pain can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation, depending on the underlying cause and the intensity of the cough.
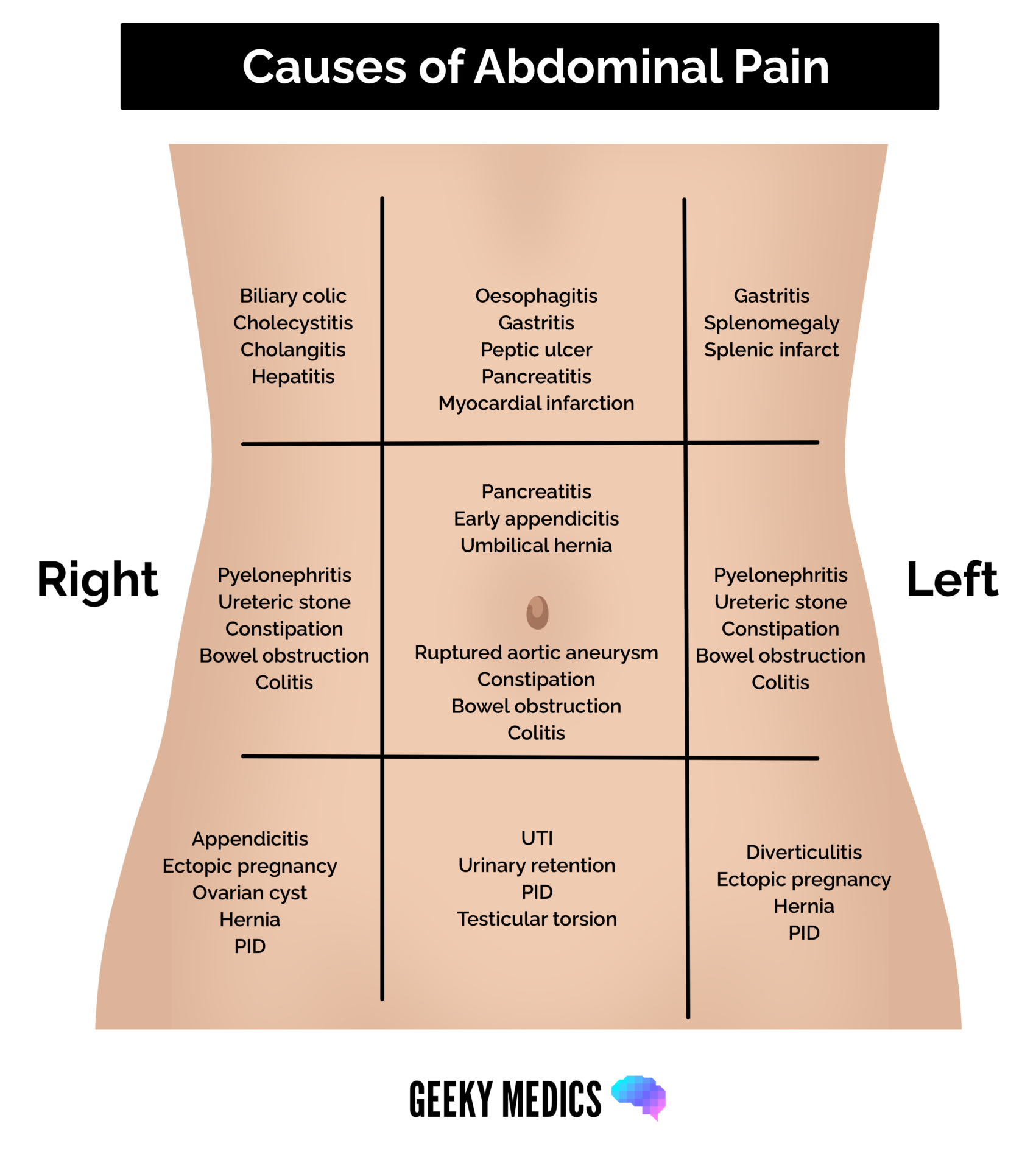
A closer look at some of the specific conditions associated with abdominal pain when coughing reveals several common culprits.
1. Muscle Strain
Perhaps the most straightforward cause is muscle strain. A prolonged or intense coughing fit can put significant stress on the abdominal muscles. Repeated contractions can lead to tiny tears in the muscle fibers, causing pain and inflammation. This is particularly common in individuals with persistent coughs, whether from a cold, the flu, or a chronic respiratory condition. The pain may worsen with each cough and can linger even after the coughing subsides.
- Find Spiritual Stores Near You Your Guide To Inner Peace
- Jamie Rhoden The Rising Stars Journey Career
2. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD, a condition in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, is another significant contributor. The increase in abdominal pressure during coughing can worsen acid reflux, irritating the already sensitive lining of the esophagus and potentially triggering pain in the upper abdomen. This type of pain might feel like a burning sensation and may be accompanied by other GERD symptoms, such as heartburn and a sour taste in the mouth.
3. Hernias
A hernia represents a more serious potential cause. It occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Coughing can exert extra pressure on the abdomen, potentially exacerbating an existing hernia, particularly in the abdominal region. This may cause a sudden, sharp pain that intensifies with coughing and can be accompanied by a visible bulge.
Recognizing the symptoms is crucial for assessing the severity of abdominal pain linked to coughing. While some discomfort may be temporary, certain signs should prompt a medical evaluation.
- Sharp or Dull Pain: The nature of the pain can vary. Sharp pain often suggests a more acute issue, such as a muscle strain or hernia. Dull pain may be associated with gastrointestinal issues or less severe muscle strain.
- Increased Pain During or After Coughing: This is a hallmark symptom. If the pain intensifies with each cough, it strongly suggests a link to the act of coughing and the increased pressure it generates.
- Bloating or Gas: These symptoms may suggest underlying digestive issues that are aggravated by coughing, such as GERD or other intestinal disturbances.
- Nausea or Vomiting: These can be signs of a more serious underlying condition and should not be ignored.
- Difficulty Breathing: If coughing is accompanied by difficulty breathing, it warrants immediate medical attention. This could be indicative of a serious respiratory or abdominal issue.
When faced with abdominal pain when coughing, a thorough diagnosis is essential. A healthcare provider will begin with a comprehensive evaluation.
1. Medical History
The doctor will gather a detailed medical history, inquiring about previous abdominal problems, surgeries, and any underlying conditions. This information helps identify potential risk factors and clues to the source of the pain.
2. Physical Examination
A physical examination includes a careful assessment of the abdomen. The doctor will gently palpate the area to check for tenderness, swelling, or any unusual masses. They may also look for signs of a hernia or assess for muscle strain.
3. Diagnostic Tests
Further diagnostic tests might be necessary to pinpoint the exact cause. These may include:
- Ultrasound: Useful for visualizing the abdominal organs and detecting abnormalities such as hernias.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the abdomen to identify problems that might not be visible on an ultrasound.
- Endoscopy: Involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera to examine the esophagus and stomach, helpful in diagnosing GERD or other digestive issues.
- Blood Tests: Help to identify infection or inflammation or to assess for organ damage.
Once a diagnosis is reached, appropriate treatment options can be considered. The approach will depend on the specific cause of the abdominal pain.
1. Medications
Medications often play a key role in symptom management:
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: For muscle strain, these medications can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Antacids or Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): For GERD, these drugs reduce stomach acid production, easing the pain.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers may be used for acute discomfort.
2. Surgical Intervention
In cases of hernias or other structural abnormalities, surgery may be the only effective solution. The goal is to repair the defect and prevent further complications.
In addition to medical treatments, several self-care strategies can ease the discomfort and promote healing. These remedies can often be used alongside medical interventions to maximize relief.
1. Rest and Recovery
Allowing your body time to heal is crucial. Avoid activities that strain your abdominal muscles, and make sure to rest whenever your body is telling you to.
2. Gentle Stretching
Some gentle stretches can help relieve muscle tension and improve flexibility. However, it's essential to consult a physical therapist before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure you do not cause further harm to the muscles.
3. Dietary Adjustments
If GERD is a contributing factor, dietary changes can provide relief. Avoiding trigger foods, such as spicy or acidic meals, and eating smaller, more frequent meals can help reduce the production of stomach acid.
Taking proactive steps can help reduce the chances of future episodes of abdominal pain when coughing. These preventive measures can contribute to overall well-being.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining good posture reduces strain on the abdominal muscles, making them less vulnerable to injury.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining optimal digestive function.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking irritates the respiratory system and can worsen coughing, contributing to abdominal pain.
While some abdominal pain related to coughing may resolve on its own, certain symptoms warrant a prompt visit to a healthcare provider.
- Persistent or Worsening Pain: If the pain continues, or increases in intensity, seek medical advice.
- Fever or Chills: These symptoms may signal an infection and should be evaluated.
- Severe Nausea or Vomiting: Could indicate a more serious problem.
- Blood in Vomit or Stool: This is a serious sign that requires immediate attention.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is key to long-term relief and preventing future episodes.
1. Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity, particularly exercises that strengthen your core muscles, can reduce the risk of muscle strain. Focus on low-impact exercises such as walking or swimming.
2. Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate gastrointestinal issues and increase the likelihood of abdominal pain. Practice relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises.
3. Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables supports digestive health and reduces the risk of conditions like GERD.
Abdominal pain when coughing can be an unwelcome experience. By learning its causes and how to address it, you can take control of your health. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking professional medical care when necessary, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can effectively minimize the chance of experiencing such discomfort in the future.
- Belly Inflation In Industries Causes Prevention Your Company
- Mens Arm Tattoos Guide Designs Styles Ideas For 2024