Is a cough accompanied by abdominal pain more than just a fleeting discomfort? Absolutely. It could signal a range of underlying issues, demanding your attention and a deeper understanding.
The experience of pain in the abdomen when coughing is, undoubtedly, a disconcerting one. It can disrupt daily routines, making even simple tasks feel challenging. The discomfort may manifest as a sharp, stabbing sensation, a dull ache that lingers, or a persistent throb that refuses to subside. The causes of this type of pain are diverse, encompassing everything from minor muscular strains to more serious, underlying medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes, the symptoms that accompany them, and the appropriate diagnostic and treatment options is crucial for effective management and, most importantly, for regaining your comfort and well-being.
This article will serve as your guide to navigating the complexities of abdominal pain triggered by coughing. We will delve into the potential sources of this discomfort, examining the physiological mechanisms at play. We will then explore the various symptoms that might accompany the pain, helping you to recognize the severity and nature of your condition. Furthermore, we will review the diagnostic methods that healthcare professionals employ to pinpoint the root cause, ensuring accurate identification. And finally, we will examine the treatment options available, from conservative approaches to more advanced medical interventions, providing a roadmap for managing the condition effectively.
- Sabrina Carpenter From Disney Star To Global Icon
- Post Malone Nashville Music City Influence Career Impact
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Condition | Abdominal Pain When Coughing |
| Common Causes | Muscle Strain, Hernia, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) |
| Symptoms | Sharp or Dull Pain, Nausea or Vomiting, Swelling or Lumps (if a hernia is present) |
| Diagnostic Methods | Physical Examination, Imaging Tests (Ultrasounds, CT Scans), Endoscopy |
| Treatment Options | Medications (Pain Relievers, Antacids, Proton Pump Inhibitors), Surgical Intervention, Physical Therapy |
| Prevention Strategies | Regular Exercise, Avoiding Straining, Quitting Smoking |
| Dietary Considerations | Avoiding Trigger Foods, Eating Smaller Meals, Staying Hydrated |
| Lifestyle Changes | Weight Management, Proper Lifting Techniques |
| Home Remedies | Warm Compress, Ginger Tea, Rest |
| When to See a Doctor | Severe Pain, Difficulty Breathing, Unexplained Weight Loss |
| Reference | Mayo Clinic |
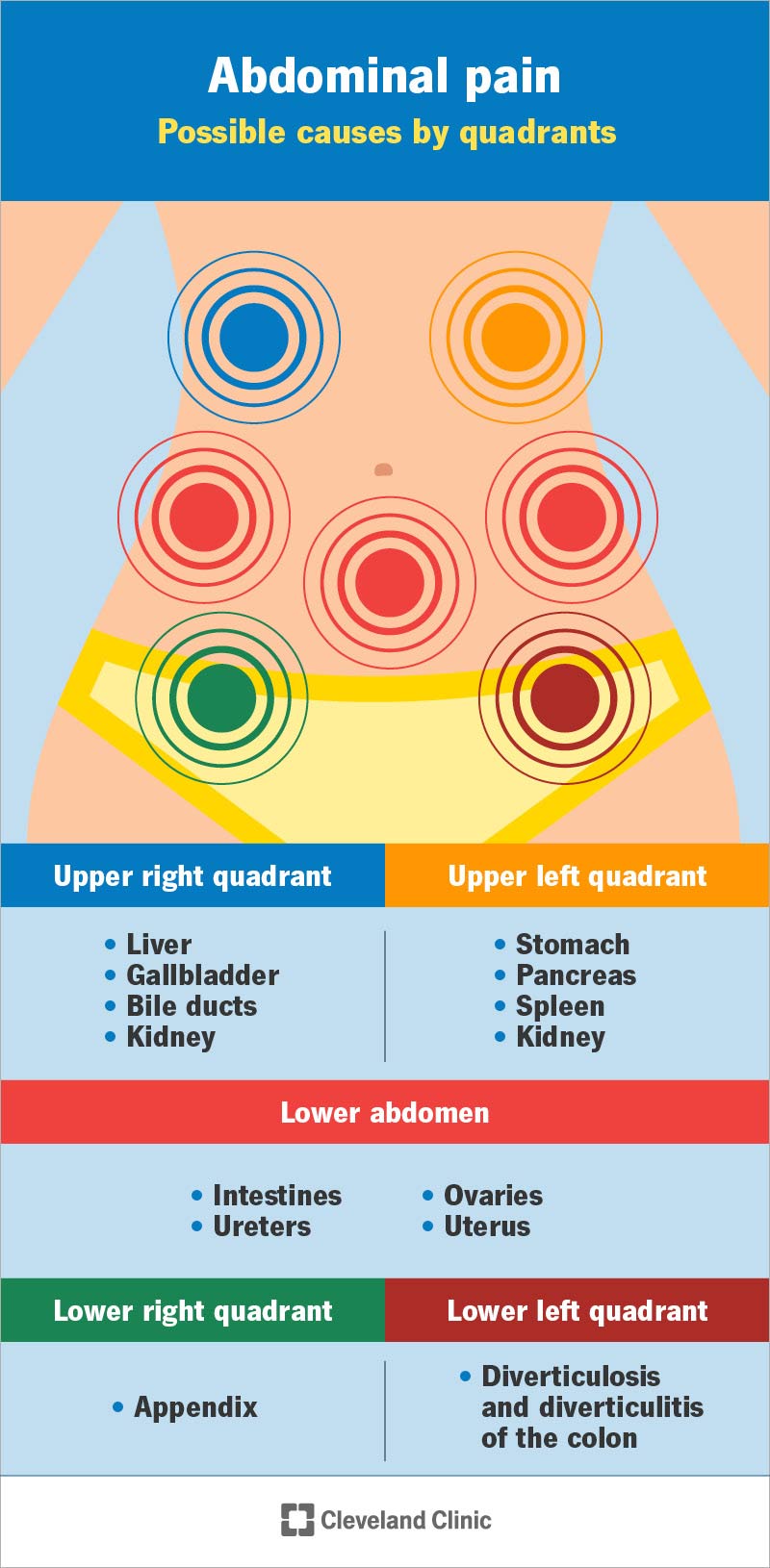
The genesis of abdominal pain when coughing can be traced to several underlying factors. Each cause demands a specific approach to management, underscoring the importance of accurate diagnosis. The following list details some of the most common reasons:
Muscle Strain
Perhaps the most frequent culprit behind abdominal pain experienced during coughing is muscle strain. The act of coughing, especially when prolonged or particularly forceful, places significant stress on the abdominal muscles. This repeated strain can lead to microscopic tears in the muscle fibers, resulting in localized discomfort and pain. The pain associated with muscle strain is typically confined to the affected area and often improves with rest and conservative measures.
Hernia
A hernia, in essence, signifies a structural weakness within the body's framework. It arises when an internal organ or part of an organ protrudes through an opening or weak spot in the muscle or tissue wall that normally contains it. The pressure exerted during coughing can exacerbate this situation, forcing the organ further through the weakened area and resulting in abdominal pain. Common types of hernias that may cause this kind of pain include inguinal hernias (in the groin area) and umbilical hernias (near the navel).
- Convert 158cm To Feet Your Ultimate Guide To Height Conversion
- Cristiano Ronaldos Noodle Hair Fashion Football Fusion
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a chronic digestive disorder characterized by the frequent backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, the tube that connects the mouth and stomach. This reflux, or backwash, of acidic contents can irritate the esophageal lining, leading to a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain. The act of coughing can further aggravate this condition by increasing intra-abdominal pressure and potentially forcing stomach acid upwards, intensifying the discomfort.
Identifying the specific symptoms that accompany abdominal pain when coughing is crucial for assessing the condition's severity and potential underlying causes. These symptoms, which vary from person to person, can offer valuable insights into the nature of the problem. Recognizing these warning signs can inform the need for medical attention and prompt appropriate care. It is important to be vigilant about the following symptoms:
- Sharp or Dull Pain: The character of the pain can vary significantly. It might present as a sudden, sharp, and intense sensation, or as a dull, persistent ache. The intensity of the pain is not always indicative of the severity of the underlying condition.
- Nausea or Vomiting: The onset of nausea or vomiting along with abdominal pain suggests a more complex condition. These symptoms can be associated with various causes, including GERD, muscle strain, or even more serious issues.
- Swelling or Lumps: The presence of swelling or a noticeable lump in the abdominal area often points to a hernia. A hernia occurs when an internal organ pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or tissue wall.
An accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective treatment. Healthcare professionals employ a range of diagnostic methods to pinpoint the root cause of abdominal pain when coughing. These methods, ranging from simple physical examinations to advanced imaging techniques, provide the necessary information to guide the course of treatment:
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination remains a crucial first step in the diagnostic process. This examination allows the physician to identify potential signs of muscle strain or the presence of a hernia. The doctor will often palpate (press) on different areas of the abdomen to locate the precise source of the pain and assess the tenderness of the area. This can often reveal the extent and nature of the problem.
Imaging Tests
When a more detailed view of the internal structures is needed, imaging tests become invaluable. Ultrasounds and CT scans can provide detailed images of the abdominal organs and tissues. These imaging modalities are particularly useful for detecting hernias, identifying any abnormalities in the abdominal cavity, and ruling out other potential causes of the pain. The choice of which imaging test to use depends on the suspected cause and the specific information the healthcare provider needs.
Endoscopy
If GERD is suspected as a contributing factor to the abdominal pain, an endoscopy might be performed. During an endoscopy, a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached (an endoscope) is inserted through the mouth and into the esophagus and stomach. This allows the physician to directly visualize the lining of these organs, looking for signs of irritation, inflammation, or damage that could be indicative of acid reflux.
Treatment options for abdominal pain when coughing are highly dependent on the underlying cause. A comprehensive approach, tailored to the specific diagnosis, is paramount for achieving relief and resolving the issue effectively. The following are some common treatment strategies:
Medications
For muscle strains, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can effectively manage the discomfort. When GERD is the culprit, medications that reduce stomach acid production become the primary course of action. Antacids can provide immediate relief by neutralizing stomach acid. More potent options, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), may be prescribed to reduce acid production in the stomach, allowing the esophagus to heal.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention becomes necessary in more severe cases or when specific underlying conditions are present. For hernias, surgery is generally required to repair the defect in the muscle or tissue wall. The surgeon may use mesh to reinforce the weakened area, preventing the hernia from reoccurring. In cases of severe GERD, surgery may be performed to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter, the muscle that prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be a valuable tool for managing abdominal pain, especially when muscle strain is a contributing factor. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises designed to strengthen the abdominal muscles and improve overall core stability. Strengthening the core muscles can also help to prevent future muscle strains and reduce the risk of recurring pain.
Proactive measures can play a significant role in reducing the incidence and severity of abdominal pain when coughing. By addressing the physical and environmental factors that contribute to the condition, you can minimize your risk and promote overall well-being. Implementing these preventative strategies can make a meaningful difference:
- Exercise Regularly: Consistent physical activity is essential for strengthening the abdominal muscles and improving overall core strength. Aim for a balanced exercise routine that includes both cardiovascular exercise and strength training.
- Avoid Straining: Be mindful of activities that place undue stress on your abdominal muscles. This includes heavy lifting, prolonged periods of intense coughing, and activities that involve twisting or sudden movements.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can trigger coughing, which can exacerbate existing abdominal pain and worsen respiratory health. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective steps you can take to improve your health.
Dietary choices can be incredibly influential in the management of conditions like GERD, which frequently lead to abdominal pain when coughing. By making informed choices about what you eat, you can mitigate your symptoms and improve your overall health. Adhering to these dietary guidelines can provide significant relief:
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Certain foods are known to worsen GERD symptoms. These include foods high in fat, spicy foods, and highly acidic foods like citrus fruits and tomatoes. Identify your individual trigger foods and limit or avoid them.
- Eat Smaller Meals: Consuming smaller, more frequent meals can reduce the pressure on your stomach, making it less likely for stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is vital for maintaining good digestive health. Water helps to dilute stomach acid and promotes overall digestive function.
Adopting specific lifestyle changes can significantly impact the frequency and intensity of abdominal pain when coughing. Making these adjustments in your daily habits can provide substantial relief:
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the pressure on the abdominal area. This can minimize the risk of developing hernias and also reduce strain on the abdominal muscles, minimizing the likelihood of pain when coughing.
Proper Lifting Techniques
When lifting heavy objects, always use proper techniques. Bend at your knees, keep your back straight, and engage your core muscles. Avoid twisting your body while lifting. Proper lifting techniques prevent unnecessary strain on the abdominal muscles, reducing the risk of pain.
For mild cases of abdominal pain when coughing, several home remedies can provide comfort and relief. While these remedies are not a substitute for medical care, they can help alleviate symptoms and support the healing process:
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help to soothe muscle pain and reduce inflammation.
- Ginger Tea: Ginger has natural anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce discomfort. Ginger tea is easy to make and can be consumed several times a day.
- Rest: Allowing your body to rest is crucial for healing. Avoid strenuous activities and give your body time to recover.
While some cases of abdominal pain when coughing may resolve on their own, it's important to be aware of when to seek medical attention. Certain symptoms can indicate a more serious underlying condition, requiring immediate medical intervention. Here's when to consult a doctor:
- Severe Pain: If the abdominal pain is intense and persistent, it's essential to seek medical advice.
- Difficulty Breathing: Difficulty breathing accompanied by abdominal pain may indicate a more serious condition.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a sign of an underlying health issue.
- Bop On Tiktok Meaning How To Create Viral Content
- Learn Chinese Swear Words The Ultimate Guide Amp Fuck You