Is that sharp jab in your abdomen when you cough just a fleeting discomfort, or a signal of something more serious? The truth is, abdominal pain triggered by coughing can be a symptom of several underlying conditions, and understanding the potential causes is the first step towards effective management and relief.
The experience of pain in the abdomen when coughing is, unfortunately, not uncommon. It can manifest in various ways, ranging from a dull ache to a sharp, piercing sensation that can be quite alarming. This article will delve into the intricacies of this symptom, providing a comprehensive overview of the possible causes, the associated symptoms, and the treatment options available. Our aim is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate this often confusing and uncomfortable experience with greater clarity and confidence.
Let's begin by understanding the basic premise. Coughing, by its very nature, is a forceful act. It involves a significant amount of physical exertion, primarily concentrated in the chest and abdominal region. This can lead to pain in several ways, from the simple strain of muscles to more complex issues related to internal organs.
- Zachary Levi Bowers Unveiling The Rising Star His Career Your Site Name
- Matthew Hollgarth Visionary Leader In Business Insights Achievements
| Understanding the Key Aspects of Abdominal Pain When Coughing | |
|---|---|
| Definition | Pain experienced in the abdominal region during or after coughing. |
| Intensity | Varies from mild discomfort to severe, sharp, or stabbing pain. |
| Duration | Can be brief or persistent, depending on the underlying cause. |
| Common Causes | Hernias, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), Costochondritis, muscle strain. |
| Associated Symptoms | Nausea, vomiting, bloating, and difficulty breathing. |
The physical act of coughing, a reflex designed to clear the airways, places considerable stress on the muscles and tissues of the abdomen. This can sometimes result in a direct, localized pain. The pain experienced can vary in intensity, ranging from a dull, lingering ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation, depending on the underlying factors at play.
Several factors contribute to the development of abdominal pain when coughing. The most common is simply muscular strain, brought about by the forceful contractions involved in coughing. Other contributors may include underlying gastrointestinal issues, as well as infections or localized inflammation. The triggers can be multifaceted, requiring accurate diagnosis for effective treatment.
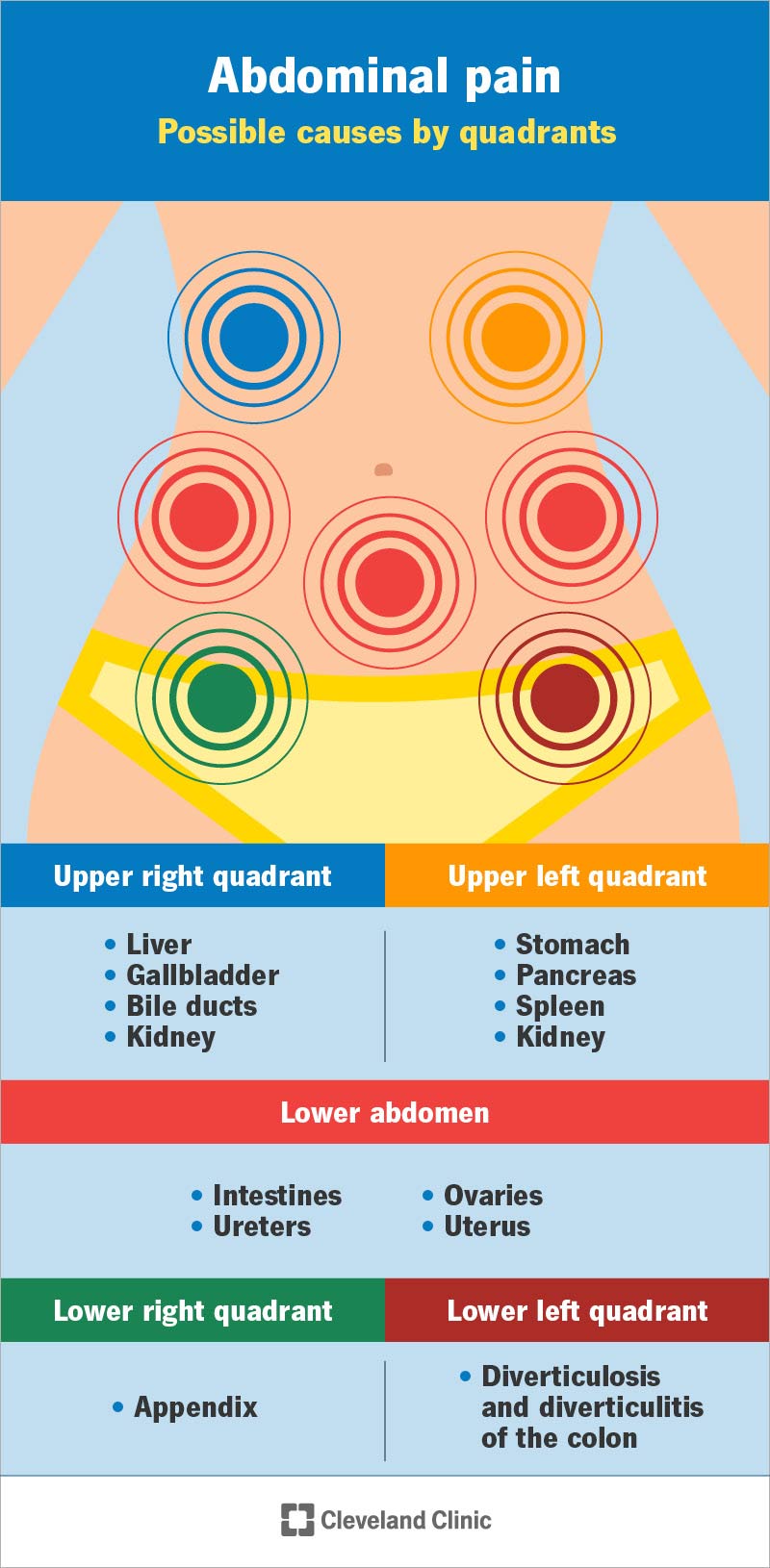
Many potential causes can lead to this form of discomfort. It's important to understand the most common culprits to facilitate proper diagnosis and treatment. These conditions range from relatively minor problems to more serious medical concerns.
- Mental Health Matters Hoodie Support Awareness
- Short Mullet Hairstyles For Men Trend Guide Styling Tips
Hernias
A hernia represents a situation where an internal organ, such as a portion of the intestine, pushes through a weakened area in the muscle or tissue that normally holds it in place. Coughing, with its characteristic increase in intra-abdominal pressure, can exacerbate the symptoms of a hernia, thus leading to heightened pain in the abdomen. In severe cases, this can result in a situation that needs immediate medical attention.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a chronic condition marked by the frequent backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus. This acid reflux causes irritation and discomfort, and coughing can worsen these symptoms. The cough itself can be a result of the irritation caused by the acid, adding an extra layer of discomfort and potentially exacerbating the abdominal pain. It's a vicious cycle.
Costochondritis
Costochondritis involves the inflammation of the cartilage connecting your ribs to your breastbone. The repetitive strain of coughing can put pressure on these already inflamed areas, leading to pain that may radiate into the abdominal region. While often felt in the chest, this pain can sometimes be perceived as originating in the abdomen.
Muscle Strain
The forceful nature of coughing can lead to strains in the abdominal muscles. Just as any strenuous physical activity can cause muscle soreness, coughing can cause the abdominal muscles to experience a similar effect. This can be particularly true if the coughing is frequent or prolonged.
Beyond the immediate pain, other symptoms may accompany the discomfort. Being aware of these additional signs can help you to monitor your condition and seek medical attention when necessary.
- Nausea: A feeling of unease in the stomach, often accompanied by the urge to vomit.
- Vomiting: The forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or distention in the abdomen, often caused by gas buildup.
- Difficulty breathing: Challenges in taking in or exhaling air, which can be caused by various underlying issues, including those that affect the abdomen.
It's important to monitor these symptoms closely, as they may indicate a more serious underlying condition. Any changes in these symptoms, or the addition of new symptoms, should be brought to the attention of your doctor.
Diagnosing the root cause of abdominal pain when coughing requires a comprehensive approach. Your healthcare provider will likely use a combination of techniques to arrive at an accurate diagnosis. This may begin with a thorough review of your medical history and a physical examination.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will check for tenderness, swelling, and other abnormalities in your abdomen.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, ultrasounds, or CT scans may be used to visualize internal organs and identify potential problems, such as hernias.
- Endoscopic Procedures: These may be necessary to examine the esophagus and stomach for conditions like GERD.
- Blood Tests: Can help detect infections or other systemic issues.
These diagnostic tools play a crucial role in helping identify the root cause of the pain, which informs the selection of appropriate treatment options. Early and accurate diagnosis is vital for the best possible outcomes.
Treatment for abdominal pain when coughing is highly dependent on the underlying cause. There is no one-size-fits-all approach. The strategy your doctor will recommend will be tailored to your specific situation.
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary. For example, if GERD is the underlying cause, your doctor may prescribe proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers to reduce stomach acid production.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can often alleviate symptoms and prevent further discomfort. These may include:
- Avoiding Heavy Lifting: This minimizes strain on abdominal muscles.
- Practicing Good Posture: Proper posture can help reduce strain.
- Engaging in Gentle Stretching Exercises: Stretching can help to strengthen abdominal muscles.
It's important to remember that these lifestyle changes should be combined with appropriate medical care for the best results. If the pain stems from a hernia, surgery might be necessary to resolve the problem.
Prevention is a key element in managing abdominal pain when coughing. While you can't always eliminate the possibility, you can take steps to reduce its likelihood and severity. These strategies are designed to help strengthen your core and promote overall health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: This reduces pressure on the abdominal muscles.
- Exercise Regularly to Strengthen Abdominal Muscles: A strong core can better withstand the force of coughing.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: These habits can contribute to various health problems that may exacerbate abdominal pain.
By adopting these preventive measures, you can lower the probability of experiencing abdominal pain during coughing episodes. These preventive measures are most effective when adopted proactively.
While some instances of abdominal pain when coughing might resolve on their own, others necessitate professional medical attention. Recognizing the warning signs and knowing when to seek help is crucial for your health.
- Severe or Persistent Pain: Pain that does not improve or worsens over time.
- Blood in Vomit or Stool: This can indicate a serious internal problem.
- Significant Swelling or Tenderness in the Abdomen: This may signal infection or other complications.
- Fever: May indicate an infection.
Timely intervention can prevent complications and ensure proper treatment, preventing more serious health problems from developing.
In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve your condition. These adjustments can work in synergy with the medical treatment to improve your comfort.
Healthy Eating Habits
Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber and nutrients can support digestive health and reduce the risk of abdominal pain. Avoid spicy or fatty foods that may trigger GERD symptoms. Some specific recommendations:
- Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of saturated fats.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to avoid overfilling your stomach.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate gastrointestinal issues. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to manage stress levels effectively. These techniques can reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Here are some additional stress-reducing strategies:
- Get enough sleep.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Spend time outdoors in nature.
- Connect with supportive friends and family.
- Bop On Tiktok Meaning How To Create Viral Content
- Honey Pine Makeup Your Guide To Natural Beauty Skincare