Does the term "AWD" all-wheel drive hold the key to enhanced vehicle performance and safety, or is it merely a marketing buzzword? The answer, as we'll explore, is a resounding yes.
All-wheel drive (AWD) systems have fundamentally altered the automotive landscape, offering drivers a significant advantage in terms of traction and control. This technology, whether on slick city streets, challenging off-road terrain, or the open highway, markedly improves a vehicle's capabilities and safeguards occupants. This exploration seeks to demystify the intricacies of AWD, providing consumers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions when considering their next vehicle purchase.
As we delve deeper into the realm of AWD, we'll examine its features in relation to two-wheel drive (2WD) and four-wheel drive (4WD) systems. The aim is to furnish a comprehensive understanding of why AWD has gained popularity in modern vehicles and the potential benefits it offers to the driving experience. This will enable drivers to confidently navigate a variety of conditions and make a choice that best suits their needs.
- Sweet Pea Puppy Bowl Your Guide To The Pawsome Event
- I Aint Reading All That Meme Origins Popularity Impact
Table of Contents
- What is AWD?
- How Does AWD Work?
- Types of AWD Systems
- AWD vs 2WD: Understanding the Differences
- AWD vs 4WD: Key Distinctions
- Benefits of AWD
- Disadvantages of AWD
- Popular AWD Vehicles
- Maintenance Tips for AWD Vehicles
- Conclusion
What is AWD?
AWD, or All-Wheel Drive, represents a drivetrain technology that distributes power to all four wheels of a vehicle. In contrast to traditional two-wheel drive systems, which power only two wheels, AWD provides superior traction by simultaneously engaging all wheels. This system is particularly beneficial in difficult weather conditions, such as heavy snow, torrential rain, or uneven surfaces where grip is compromised.
Modern AWD systems are engineered to adapt to changing driving environments, ensuring optimal performance and promoting safety. Depending on the manufacturer and model, AWD can be implemented as full-time, part-time, or on-demand, each with unique advantages based on the specific needs of the driver and the anticipated conditions.
History of AWD Technology
The genesis of AWD technology dates back to the early 20th century. The inaugural AWD vehicle was introduced in 1903 by Dutch engineer Jacobus Spijker. Over the subsequent decades, advances in engineering and technology have transformed AWD into a sophisticated system now utilized in a diverse range of vehicles, from compact cars to luxury SUVs. This evolution highlights the ongoing pursuit of enhanced vehicle control and driver confidence across various conditions.
How Does AWD Work?
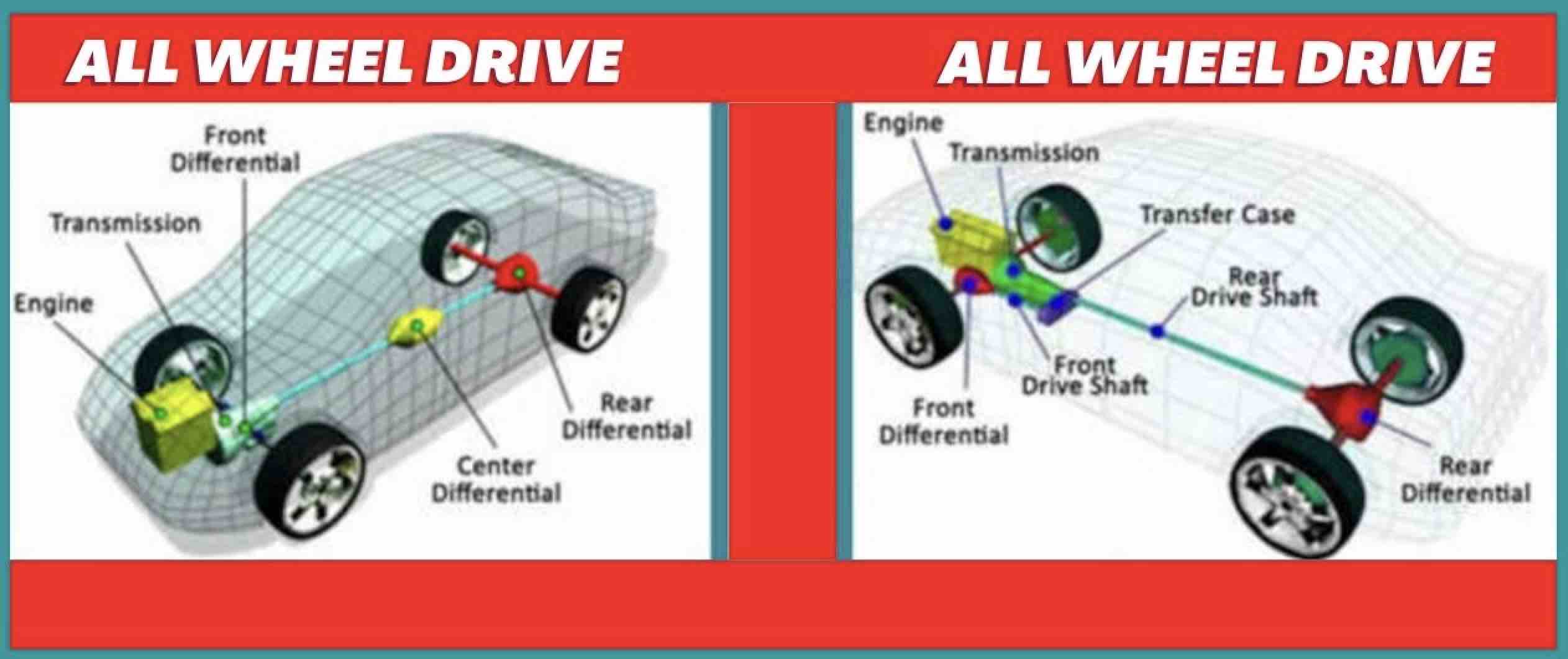
AWD systems operate through a blend of mechanical and electronic components that work together to distribute power to all four wheels. The process initiates with the engine generating power, which is then channeled to the transmission. Subsequently, power is directed to both the front and rear axles via a series of differentials and drive shafts.
A central feature of AWD is its capability to adjust power distribution based on prevailing road conditions. For instance, when one wheel loses traction, the system can automatically redirect power to wheels with superior grip, maintaining stability and allowing the driver to retain control of the vehicle. This intelligent power management is crucial for navigating slippery or uneven surfaces effectively.
Key Components of AWD Systems
- Center Differential: Distributes power between the front and rear axles.
- Front and Rear Differentials: Allow wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds.
- Drive Shafts: Transfer power from the transmission to the axles.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): Monitors wheel speed and adjusts power distribution in real-time.
Types of AWD Systems
The effectiveness of AWD systems is not uniform across all vehicles. Manufacturers offer various AWD system types depending on the vehicle's design and intended usage. Here are some of the most common types found in today's vehicles:
Full-Time AWD
Full-time AWD systems continuously supply power to all four wheels, providing consistent traction and optimal control. This configuration is ideally suited for drivers who prioritize consistent performance and safety in all driving scenarios, ensuring maximum grip and stability at all times.
Part-Time AWD
Part-time AWD systems typically operate in two-wheel drive mode under normal driving conditions, switching to four-wheel drive when additional traction is required. This system is frequently employed in vehicles designed for off-road purposes, offering the flexibility to adapt to both paved roads and more challenging terrains.
On-Demand AWD
On-demand AWD systems behave as two-wheel drive vehicles until extra traction becomes necessary. This type of AWD is commonly found in passenger cars and crossovers. These systems offer advantages such as improved fuel efficiency under normal driving conditions, and also provide enhanced performance whenever the need for increased traction arises.
AWD vs 2WD
Two-wheel drive (2WD) systems deliver power to either the front or rear wheels, making them simpler in design and more cost-effective to manufacture than AWD systems. However, 2WD vehicles may encounter challenges with traction in adverse conditions such as snow, mud, or uneven terrain, reducing driver control and safety.
In contrast, AWD systems offer superior traction and control, making them a better option for drivers who frequently encounter challenging weather or road conditions. While AWD vehicles may incur higher initial costs and potentially lower fuel efficiency, the added safety and enhanced performance frequently justify the investment. AWD can provide peace of mind when facing difficult road conditions.
Key Differences Between AWD and 2WD
- Traction: AWD offers better traction in slippery conditions.
- Fuel Efficiency: 2WD vehicles tend to be more fuel-efficient.
- Cost: AWD systems are generally more expensive to purchase and maintain.
AWD vs 4WD
Four-wheel drive (4WD) systems are specifically engineered for off-road applications and extreme conditions. Unlike AWD, which automatically adjusts power distribution, 4WD systems usually necessitate manual engagement. This makes 4WD well-suited for navigating rugged terrain but less practical for everyday driving situations.
AWD systems, on the other hand, offer a more seamless driving experience by automatically adapting to changing road conditions without requiring driver input. While both systems power all four wheels, their applications and performance characteristics are distinct. AWD is more versatile for general usage.
Comparison of AWD and 4WD
- Usage: AWD is better suited for on-road driving, while 4WD excels in off-road environments.
- Complexity: AWD systems are generally easier to use and maintain.
- Performance: 4WD provides greater torque and low-range gearing for tackling tough obstacles.
Benefits of AWD
AWD systems provide a number of benefits, which make them a popular choice for modern vehicles. Here are some of the key advantages that drivers can appreciate:
- Improved Traction: AWD enhances grip on slippery surfaces, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Enhanced Stability: By distributing power evenly, AWD improves vehicle handling and control.
- Increased Safety: AWD vehicles are less likely to get stuck in adverse conditions, providing peace of mind for drivers.
Real-World Applications of AWD
AWD systems have demonstrated their value in a range of situations, from commuting in snowy climates to navigating muddy trails. Studies indicate that vehicles equipped with AWD experience fewer accidents and provide better handling in challenging conditions, making them a wise investment for many drivers. The ability to handle various conditions makes AWD a worthwhile asset.
Disadvantages of AWD
Though AWD systems offer significant advantages, they also have certain drawbacks. It is important to consider these points:
- Higher Cost: Vehicles with AWD typically have a higher purchase price than their 2WD counterparts.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: The added weight and complexity of AWD systems can negatively affect fuel economy.
- Increased Maintenance: AWD components necessitate routine maintenance to ensure optimal functionality.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
The decision to choose an AWD vehicle requires careful evaluation of driving needs and priorities. For those prioritizing safety and performance in challenging conditions, AWD may be the best choice. However, drivers on a budget might find 2WD vehicles more appropriate for their requirements. The optimal choice depends on balancing desired features with practical constraints.
Popular AWD Vehicles
Many manufacturers offer vehicles equipped with AWD systems, catering to a wide array of preferences and financial considerations. Below are some of the most popular AWD vehicles available in the market:
- Subaru Outback: Recognized for its robust build and excellent all-weather capabilities.
- Audi Q5: Combines luxury and performance with Quattro AWD technology.
- Volvo XC90: Delivers a smooth ride and incorporates advanced safety features.
Choosing the Right AWD Vehicle
Selecting the most appropriate AWD vehicle involves consideration of factors such as budget, intended use, and desired features. Test-driving different models allows potential buyers to determine which AWD system best suits their specific needs and driving style, resulting in more informed decision-making.
Maintenance Tips for AWD Vehicles
To ensure the optimal performance of an AWD system, consistent and proper maintenance is essential. Here are some helpful tips to keep an AWD vehicle in peak condition:
- Check Fluid Levels: Regularly inspect and replace transmission and differential fluids as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspect Drivetrain Components: Look for any signs of wear or damage to the drive shafts and joints.
- Rotate Tires: Maintain uniform tire wear to maximize traction and prolong tire life.
Importance of Professional Maintenance
Because of the complexity of AWD systems, it is critical to have these systems serviced by qualified technicians. Regular inspections and prompt repairs help to prevent costly problems and ensure the vehicle's long-term reliability. Professional maintenance is key to ensuring longevity and performance.
Conclusion
In sum, a thorough understanding of the meaning and implications of AWD can significantly enhance your driving experience. Whether navigating snowy roads or enjoying a scenic drive, AWD systems provide superior traction, stability, and safety. While there are some drawbacks to consider, the benefits often outweigh the costs for many drivers.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with AWD vehicles in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the world of automotive technology. Together, let's drive toward a safer and more informed future!
Data source: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration